Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Optics and Optical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 International Quantum Academy, Shenzhen 518048, China
3 Shenzhen Institute for Quantum Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
4 Hefei National Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230088, China
5 e-mail: atwang@ustc.edu.cn
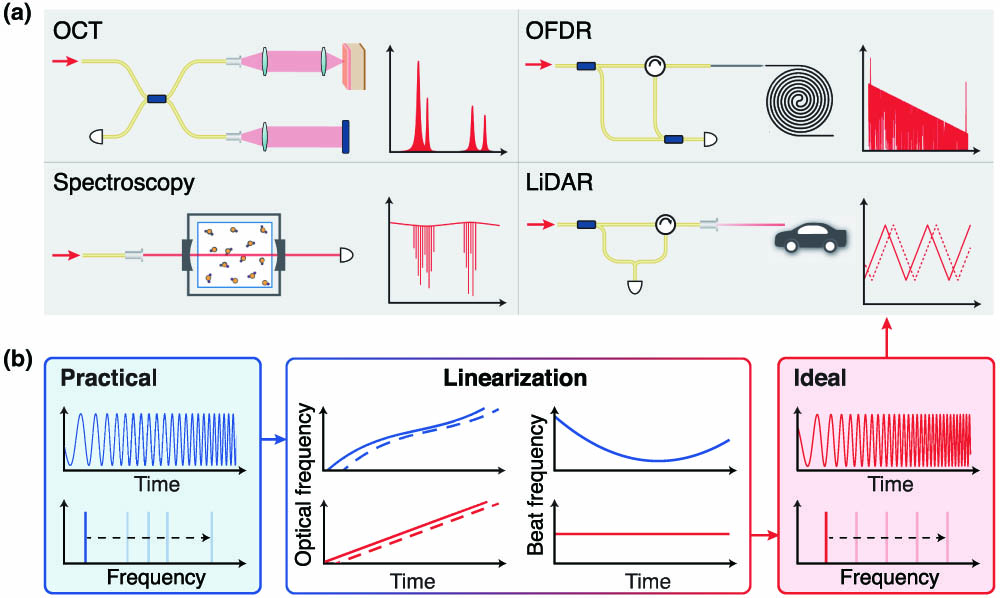
Tunable lasers, with the ability to continuously vary their emission wavelengths, have found widespread applications across various fields such as biomedical imaging, coherent ranging, optical communications, and spectroscopy. In these applications, a wide chirp range is advantageous for large spectral coverage and high frequency resolution. Besides, the frequency accuracy and precision also depend critically on the chirp linearity of the laser. While extensive efforts have been made on the development of many kinds of frequency-agile, widely tunable, narrow-linewidth lasers, wideband yet precise methods to characterize and linearize laser chirp dynamics are also demanded. Here we present an approach to characterize laser chirp dynamics using an optical frequency comb. The instantaneous laser frequency is tracked over terahertz bandwidth at 1 MHz intervals. Using this approach we calibrate the chirp performance of 12 tunable lasers from Toptica, Santec, New Focus, EXFO, and NKT that are commonly used in fiber optics and integrated photonics. In addition, with acquired knowledge of laser chirp dynamics, we demonstrate a simple frequency-linearization scheme that enables coherent ranging without any optical or electronic linearization unit. Our approach not only presents novel wideband, high-resolution laser spectroscopy, but is also critical for sensing applications with ever-increasing requirements on performance.
Photonics Research
2024, 12(4): 663
上海理工大学光电信息与计算机工程学院,上海 200093
采用有限时域差分(FDTD)法仿真了不同闪耀光栅结构上的银(Ag)薄膜模型。在633 nm的激发光下,闪耀光栅上周期为1/1200 mm、厚度为15 nm的Ag薄膜模型产生了较强的局域表面等离子体共振(LSPR)效应。利用机械刻划工艺和电子束蒸发镀膜工艺成功制备了这种Ag光栅薄膜,从而大幅降低了图案化电场增强薄膜的制备成本和难度。利用该电场增强Ag薄膜,基于表面增强拉曼散射(SERS),对亚甲基蓝染料进行检测,SERS信号强度增强,与FDTD仿真结果吻合。同时,基底不同位置处的主要特征峰强度的相对标准偏差(RSD)值都小于17%,薄膜表现出良好的均匀性和再现性。
薄膜 局域表面等离子体共振 有限时域差分法 金属薄膜 闪耀光栅 表面增强拉曼散射 中国激光
2023, 50(23): 2303101
针对无人机在复杂多障碍环境下的路径规划问题, 提出基于改进粒子群的优化算法。首先, 通过统一障碍物环境建模、优化适应度函数, 并采用混沌粒子初始化使粒子群多样化, 增强了算法的稳定性; 然后, 用自适应加速度系数替代传统粒子群算法的加速度常数, 避免陷入局部极小值, 同时提高了算法收敛到全局最优解的效率; 最后, 用无人机运动编码代替传统粒子群算法中粒子搜索轨迹的编码方式, 提高解的最优性, 搜索最优解路径。仿真结果表明: 当进行无人机路径规划时, 改进粒子群算法可以有效解决复杂的多障碍环境中传统粒子群算法的问题, 与灰狼优化算法、差分进化算法、量子粒子群算法和传统粒子群算法相比, 改进后的算法在不同场景静态环境中路径寻优精度和稳定性明显提高, 且与动态粒子群算法相比, 新算法也能更好地适应动态环境。
粒子群算法 混沌粒子初始化 自适应加速度系数 运动编码 路径规划 particle swarm optimization chaotic particle initialization adaptive acceleration coefficient motion encoding path planning
微腔光频梳具有功耗低、可集成、梳齿间隔可调的特点,在各个领域都有广泛的应用。绝缘层上的硅(SOI)材料加工工艺与现有的互补金属氧化物半导体(CMOS)工艺兼容,使其成为最具前景的光子平台之一。本文设计了一种截面为脊形的硅基微环谐振腔,研究了各个几何参数对微环谐振腔色散的影响;数值求解了微环谐振腔热动态方程,并分析了不同参数对微环谐振腔热动态效应的影响。数值求解了LLE(Lugiato-Lefever Equation)模型,由于SOI微腔光频梳理论研究大多忽略了热光效应,因此本文分析了在模型中引入热光效应项后对光频梳产生和演化的影响。数值结果表明,在温度变化范围为0~0.16 ℃条件下,时域上光场最大功率值增加了22%,频域上光频梳展宽了221 nm。最后对两种热光效应条件下光频梳输出频谱进行分析,结果表明,光频梳在热光效应温度变化范围为0~0.32 ℃的情况下,相较于0~0.16 ℃的情况,带宽展宽了353 nm。
非线性光学 硅基波导 微环谐振腔 Lugiato-Lefever方程模型 热光效应 光频梳 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(17): 1719001
1 中国科学技术大学生命科学与医学部生物医学工程学院,江苏 苏州 215163
2 中国科学院苏州生物医学工程技术研究所,江苏 苏州 215163
3 东南大学附属中大医院消化内科,江苏 南京 210009
食管鳞癌(ESCC)是我国常见的消化道恶性肿瘤之一。临床上,窄带成像联合放大内镜(NBI-ME)能够显示出食管粘膜层的微血管形态变化,是诊断ESCC的重要手段。针对ESCC识别模型难以兼顾识别准确率和推理效率的问题,提出一种融合注意力机制的轻量化残差网络(CALite-ResNet)对食管NBI-ME图像进行分类。从多家医院采集到206例患者共11468张NBI-ME图像作为本研究数据集。实验结果表明,ESCC识别的准确率和敏感度分别在图像级别达到96.39%和95.70%,在病人级别达到95.70%和94.62%,单张食管图像的平均预测时间为16.42 ms。因此,CALite-ResNet模型对ESCC具有较高的识别准确率和较快的推理效率,能够为ESCC的临床辅助诊断提供有效帮助,具备一定的临床意义与应用价值。
图像处理 轻量化网络 注意力机制 食管鳞癌 窄带成像 放大内镜 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(10): 1010023

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Qaleido Photonics, Hangzhou 310000, China
2 International Quantum Academy, Shenzhen 518048, China
3 Shenzhen Institute for Quantum Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
4 Department of Optics and Optical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
5 Key Laboratory of Specialty Fiber Optics and Optical Access Networks, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
6 Key Laboratory of Radar Imaging and Microwave Photonics, Ministry of Education, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China
7 Hefei National Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230088, China
The foundry development of integrated photonics has revolutionized today’s optical interconnect and datacenters. Over the last decade, we have witnessed the rising of silicon nitride () integrated photonics, which is currently transferring from laboratory research to foundry manufacturing. The development and transition are triggered by the ultimate need for low optical loss offered by , which is beyond the reach of silicon and III-V semiconductors. Combined with modest Kerr nonlinearity, tight optical confinement, and dispersion engineering, has today become the leading platform for linear and Kerr nonlinear photonics, and it has enabled chip-scale lasers featuring ultralow noise on par with table-top fiber lasers. However, so far all the reported fabrication processes of tight-confinement, dispersion-engineered photonic integrated circuits (PICs) with optical loss down to few dB/m have only been developed on 4-inch (100 mm diameter) or smaller wafers. Yet, to transfer these processes to established CMOS foundries that typically operate 6-inch or even larger wafers, challenges remain. In this work, we demonstrate the first foundry-standard fabrication process of PICs with only 2.6 dB/m loss, thickness above 800 nm, and near 100% fabrication yield on 6-inch (150 mm diameter) wafers. Such thick and ultralow-loss PIC enables low-threshold generation of soliton frequency combs. Merging with advanced heterogeneous integration, active ultralow-loss integrated photonics could pave an avenue to addressing future demands in our increasingly information-driven society.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(4): 558
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of The Gas Disaster Detecting, Preventing and Emergency Controlling, Chongqing 400037, China
2 China Coal Technology and Engineering Group Chongqing Research Institute, Chongqing 400039, China
3 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
A novel fiber-optic magnetic field sensor with high interrogation speed and resolution by using an etched fiber Bragg grating (FBG) in conjunction with a dual-loop optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. A commercial FBG is firstly dipped into mixed hydrofluoric acid solution to remove the cladding layer and then is embedded with the magnetic fluid (MF) as a sensing element. The central wavelength reflected from the FBG is related to the overall time delay of the dual-loop OEO, which determines the oscillating frequency of the OEO. Therefore, the magnetic field can be estimated by measuring the oscillating frequency shift of OEO. The experimental results show that the oscillating frequency linearly increases with the increment of the magnetic field, achieving the sensitivity of 16.3 Hz/Oe with an R-square of 0.991 in the range of 5 mT-10 mT. In addition, the maximum error is within ±0.05 mT in the range of 7 mT-8 mT, which offers potentials in many fields where the high-precision magnetic field measurement is required.
Etched fiber Bragg grating optoelectronic oscillator magnetic fluid magnetic field measurement Photonic Sensors
2022, 12(4): 220419
华中光电技术研究所- 武汉光电国家研究中心, 湖北 武汉 430223
基于延迟积分(Time Delay Integration, TDI)机制的长波红外热像仪在**、航空、航天领域应用广泛, 通过光学扫描, 能够同时实现大的成像视场和较高的空间分辨率。基于TDI机制的长波红外热像仪的探测器采用TDI工作模式。由于TDI与光学扫描之间匹配精度的问题, 在对景物成像时, 景物的边缘常常存在参差不齐的锯齿状现象, 影响目标提取和识别, 降低了图像的观感。分析了因扫描视场和光学视场不匹配导致景物图像产生锯齿的现象, 提出了一种将探测器上像元分布的空间物理间隔转换为时间延迟的锯齿消除方法。时间换空间的方法能有效消除景物图像锯齿, 真实还原小目标边缘的细节, 大大提升了图像的观感, 该方法已广泛应用于红外搜索跟踪(IRST)系统、红外光电系统等装备。
延迟积分 扫描 匹配 锯齿 中心距 焦距 TDI scanning matching sawtooth center distance focal length





